

It has been reviewed by appropriate medical or clinical professionals and deemed accurate on the date of review. This information was published by Bupa's Health Content Team and is based on reputable sources of medical evidence.
Personal communication, Mr Yemi Kuponiyi, Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, August 2021. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Royal College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists. The management of ovarian cysts in postmenopausal women. Management of suspected ovarian masses in premenopausal women. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014 29 (4). Oral contraceptives for functional ovarian cysts. You’re most likely to be offered keyhole surgery, which is usually done as a day-case procedure. There are two ways of carrying out surgery for an ovarian cyst: They‘ll also recommend surgery if there’s a risk your cyst may be ovarian cancer. If your cyst is large, causing symptoms or doesn’t go away, your doctor will probably suggest you have surgery to remove it. Your doctor will usually only recommend surgery if the cyst is causing symptoms or is very large. Ovarian cysts during pregnancy nearly always go away without treatment. If your ovarian cyst doesn’t go away, your gynaecologist may then recommend surgery to remove it. You may also be asked to have another blood test for CA-125. every four to six months for a year if you’ve been through the menopause. after a year if you’re still having periods. Your doctor will discuss with you when you should have a repeat ultrasound scan. So, this approach helps you avoid having treatment you don’t need. Most small cysts on your ovaries disappear on their own and don't cause any problems. If your ovarian cyst is small and isn’t causing any problems, your doctor may suggest keeping a close eye on it for a while with ultrasound scans. Your personal preferences will also be considered. Whether or not you need treatment will depend on: If you have an ovarian cyst, you may not need any treatment. You can also get cysts on your ovaries if you have endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). To find out more about ovarian cysts and cancer, see our FAQ: Does having an ovarian cyst mean I have cancer? But this doesn’t necessarily mean that they’re cancerous. You may hear these types of ovarian cyst referred to as tumours. These may happen because of an overgrowth of cells. It may continue to grow and become filled with blood. A corpus luteum cyst can form if the corpus luteum doesn’t break down. A follicular cyst can happen if a follicle doesn’t release an egg but carries on growing. The two main types of functional cyst form at different stages in this cycle. If the egg isn’t fertilised, the corpus luteum begins to break down. This releases hormones that help the lining of your uterus (womb) prepare for pregnancy. After releasing the egg, the follicle normally changes into something called the corpus luteum. One of these will mature and release an egg. They don’t happen after the menopause.Įach month, your ovary produces several follicles (tiny fluid-filled sacs). 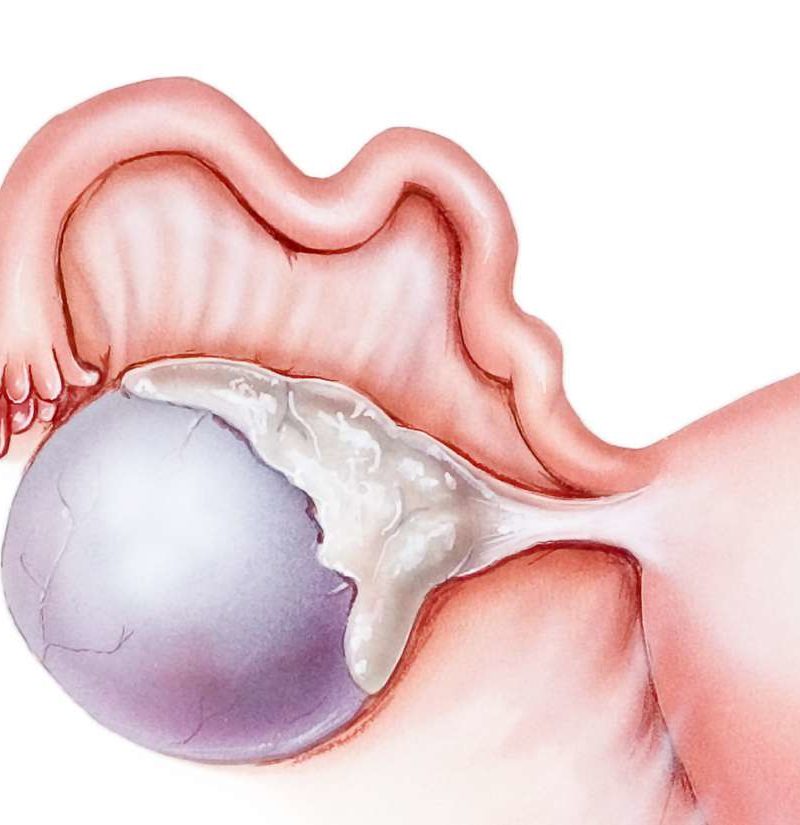
This means that they develop as part of your usual menstrual cycle. These can be split into two groups: functional cysts and pathological cysts. There are lots of different types of ovarian cyst.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
